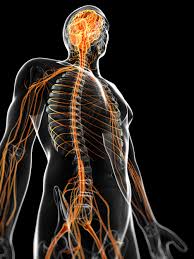
Nervous System
The functions of the nervous system include sensory input, integration, control of muscles and glands, and mental activity. It is responsible for processing and transmitting information throughout the body, playing a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and coordinating movement.
Nerves
Nerves are specialized cells designed for optimal transmission of electrical impulses.
Etymology The term “nerve” originates from the late 14th century, derived from Old French nerf and Medieval Latin nervus, meaning “sinew” or “tendon.” The Latin nervus also referred to a “cord” or “bowstring,” with its pre-Latin root neuros tracing back to the Proto-Indo-European (s)neu-, meaning “tendon” or “sinew.” The modern anatomical sense of nerves as fiber pathways conveying impulses between the brain and body emerged around 1600.
Major Divisions of the Nervous System
The nervous system can be categorized into two primary functional divisions:
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord and acts as the regulatory and processing center of the nervous system. It is responsible for interpreting sensory input, generating thoughts, and coordinating responses.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The PNS comprises nerve cells and axons that extend throughout the body. It is divided into:
- Afferent (sensory) nerves: Transmit sensory information to the CNS.
- Efferent (motor) nerves: Relay signals from the CNS to muscles, glands, and organs to execute functions.
Images of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System Image Source: OpenStax College – Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site, CC BY 3.0
Peripheral Nervous System Image Source: Own work, CC BY 3.0
Role of the Nervous System in Movement and Function
For our purposes, the nervous system is essential for:
- Receiving information from sensory afferents.
- Interpreting, organizing, and planning responses.
- Activating motor units through efferent motor nerves.
Optimal Neuromuscular Control
Optimal neuromuscular function is crucial for movement efficiency and injury prevention. According to the National Academy of Sports Medicine:
“The ability of the neuromuscular system to allow agonists, antagonists, stabilizers, and neutralizers to work synergistically to produce, reduce, and dynamically stabilize the entire kinetic chain in all three planes.”
This definition highlights the complexity of motor control, coordination, and muscular function, emphasizing the importance of a well-integrated nervous system for overall movement and health.
RELATED POSTS
View all